
EXPLORE
Secure and privacy-preserving data management and analytics.
Connect, protect and explore your data with our secure, integrated platform. Resolve data inconsistencies via data hygiene, and yield new data structures that favor analysis and various data derivations. Accelerate data-driven decision making with comprehensive data visualization for various applications – while protecting data at rest, in transit and in use.
The Problem
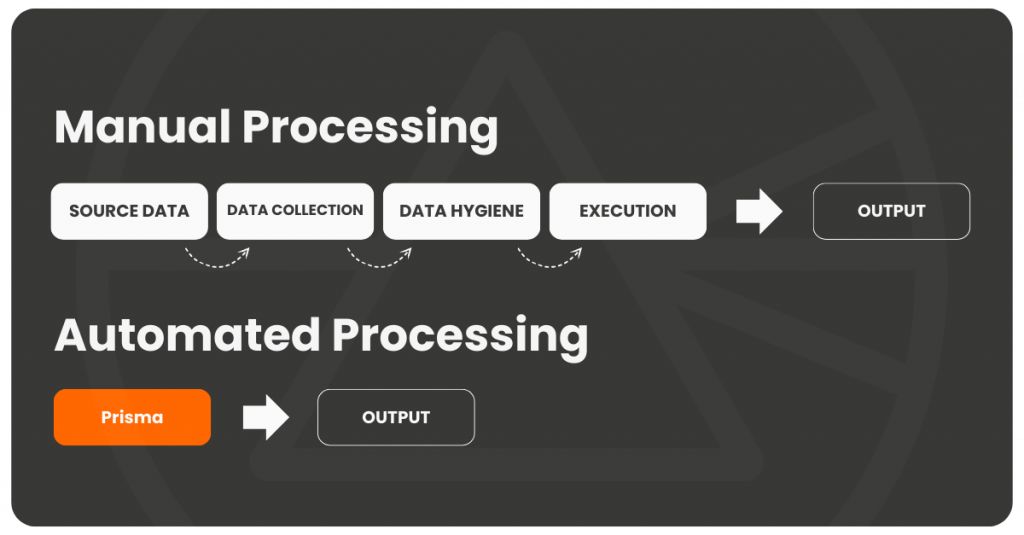
Manual data management workflows are time-consuming, prone to errors, inefficient, generate duplication, ad-hoc, and hard to inspect for errors. Algemetric’s platform enables entire workflows to be mapped and automated, becoming a process within applications. This process generates the same output as manual processing, without the problems associated with manual operations – all while fortifying data privacy and security.
Secure Data Management Prevents:
APIs: Several consumption methods, insufficient documentation, missing endpoints and attributes, incompatibility with other data sources, overlapping data delivery.
Databases: Multiple engines and connection configurations, non-interoperable queries and stored procedures create a state of rigid dependance on each database solution.
Social Media Feeds: Datasets obtained from social media feeds are highly sensitive to each of their platforms’ choices for attributes and formats.
Websites: Data is often obtained from techniques such as web crawling and web scraping which can be subject to request limitation, website updates that break how crawling and scraping work, with no guarantee that the information will be always available.
Manual and Ad-hoc Data Input: With no systems in place for obtained data, many organizations must deal with manual inputs using spreadsheets, text documents, emails, slide decks, and other everyday tools.
Lack of Hygiene: Dirty data annihilates the utility of valuable data. Data that is duplicated, incomplete, missing, inaccurate, outdated and misplaced are all examples of lack of data hygiene. Dirty data compromises the efficacy of operations and increases the overall time for executing tasks that depend on that kind of data.
Lack of Normalization: Different data sources often contain the same information in several different formats and representations. Some attributes can be also scattered, as if they were independent from each other, when they should be grouped together for context. Unnormalized data can easily lead to duplication and weakened data analysis via inconsistent information.
Lack of Standardization: How should financial data be structured? What about inventory, access control logs, web search and navigation history, sales and healthcare records? With every data source owner thinking and acting by themselves, every new integration might require changes in the entire flow of data usage due to how the same type of data is organized and delivered for consumption.
Small Subset Data: When available data does not tell the whole story. The available data corresponds to a fraction of the information required.
Out-of-date Data: It could be hours, days, weeks, months, or even years. If data is not available at the required frequency, the data served no longer represents the current state of practice.
Invalid Data: Policies, standards, laws, specifications, best practices, and other references are all subject to change. Data impacted by any of those mechanisms might be deemed invalid if it is not updated when the mechanisms are changed.
Decisions made based on insights obtained from stale data will most likely lead to incorrect results.
Got Data. Now What? Being in possession of valuable data is not enough. Organizations benefit from the proper exploration of data at hand. Unexplored data has no ultimate practical value, even if the value is fundamentally there.
Missing Expertise: Sometimes organizations know what they want from the data they have without actually knowing how to achieve it. With no proper strategy in place for handling data collection, preparation, processing, and visualization, many companies are flooded with tools with overlapping functionalities while some critical needs remain unattended.
The Solution:
Algemetric provides a secure and privacy-preserving data management and analytics platform. It handles data collection, preparation, and visualisation for providing insights, analytics, and intelligence from multiple independent data sources in a unified way. The platform provides the flexibility to handle arbitrary formats and complex patterns, ensuring that these datasets are informative. It also offers a comprehensive set of data visualisation mechanisms that can be extended to address the specific needs of various niche applications.
Connect
Take control of inefficient manual data management.
Protect
Fortify your data privacy and security.
Explore
Derive insights and intelligence from valuable and sensitive data.
How Algemetric's Platform Works
Initially, Algemetric conducts an assessment to determine your data-driven needs. Upon inspection of all functional, legal and corporate requirements, the applicable algorithms are defined in the platform. The Data Collector will then obtain data from the data sources an organisation uses in its operations. Data sources can be from external services and/or from manual input. Once data is properly obtained, it is subject to a comprehensive process of data preparation. The output of the preparation process is sent to storage as a unified data structure ready to be used. From that point on, the application is ready to operate via the dashboard where users will request reports, visualisations, and integrations with external tools where required.
Dashboard: The control room for data management. The dashboard is composed of three main components:
- Data Connector – The mechanism responsible for connecting to many arbitrary data sources and executing a series of pre-defined procedures for data preparation. The Data Connector is also able to receive new instructions and expand its data preparation capabilities.
- Data Visualization – Every main algorithm specified in in the platform has a visualization mechanism defined for the associated result data set. The default visualization objects are graphs from a wide variety of graph types. However, custom visualization options can easily be added.
- Recommendations – From collected and processed data, the platform provides recommendations whenever applicable. Data used for recommendations is tagged and can be used as an input for machine learning algorithms, providing recommendations according to predefined rules.
Storage: The unified data structure organized by the platform. A hygienic and consistent database for strategic data processing.
Platform API: The brain of the entire data processing operation. The Platform API is responsible for managing algorithms and their output – providing the dashboard information required for its operation.
Data Source Management: Add, configure, modify, and remove data sources even if no API is available. Also, input data manually via the dashboard. Manual inputs are enabled by forms that can be defined and managed on the dashboard.
Report Management: An expandable collection of customizable and collaborative reports.
Visualization Management: Decide how data is displayed by choosing from a collection of predefined graphs and tables, or by creating a new one.
Integration Management: Configure and export results directly to other tools, when desired.
Recommendation Engine: Data points are considered for data classification and training, according to selected decision targets, to establish a recommendation system.
Secure Data Processing: When working with encrypted data, data is protected in use.
M2M IAM: When working with plain data, data is protected at rest and in transit.
Automation: Well-defined procedures must be automated to save time and eliminate human error – increasing the efficiency of data workflows.
Complexity Reduction: Manage large data sets with various data sources working together. Automate data processing for insight generation and business intelligence – handled by a unified and powerful platform. Eliminate the need for a large number of tools offering partial and overlapping solutions.
User-Friendly: Engage with an easy to use and rewarding platform -without needing in-depth technical knowledge.
Versatility: We enable customized capabilities on an as-needed basis.
Augment Customer Strategic Information: No matter how valuable customer data is, add strategic value to your operations.
Data Collection: Collect and input data, either from external services or manually within the application.
Data Preparation: Automated data hygiene, unification, and readiness.
Data Processing: Includes all reports and intelligence on data.
Data Visualization: Render data results with lists, files, graphs and other visualisation objects – or export to external tools like Tableau and Microsoft Power BI.
User-friendly.
Actionable insights and intelligence.
Secure and privacy-preserving.
Automated data processing.
Efficient and scalable computation.
Identity and access management.
Simplified analytics workflows.